
The cloud isn’t right for every business, be that because of latency constraints at the edge, regulatory requirements or because it’s simply cheaper to own and operate their own data centers for their specific workloads. Given this, it’s maybe no surprise that the vast majority of enterprises today use both public and private clouds in parallel. That’s something Microsoft has long been betting on as part of its strategy for its Azure cloud, and Google, too, is now taking a number of steps in this direction.
With the open-source Kubernetes project, Google launched one of the fundamental building blocks that make running and managing applications in hybrid environments easier for large enterprises. What Google hadn’t done until today, though, is launch a comprehensive solution that includes all of the necessary parts for this kind of deployment. With its new Cloud Services Platform, though, the company is now offering businesses an integrated set of cloud services that can be deployed on both the Google Cloud Platform and in on-premise environments.
As Google Cloud engineering director Chen Goldberg noted in a press briefing ahead of today’s announcement, many businesses also simply want to be able to manage their own workloads on-premise but still be able to access new machine learning tools in the cloud, for example. “Today, to achieve this, use cases involve a compromise between cost, consistency, control and flexibility,” she said. “And this all negatively impacts the desired result.”

Goldberg stressed that the idea behind the Cloud Services Platform is to meet businesses where they are and then allow them to modernize their stack at their own pace. But she also noted that businesses want more than just the ability to move workloads between environments. “Portability isn’t enough,” she said. “Users want consistent experiences so that they can train their team once and run anywhere — and have a single playbook for all environments.”
The two services at the core of this new offering are the Kubernetes container orchestration tool and Istio, a relatively new but quickly growing tool for connecting, managing and securing microservices. Istio is about to hit its 1.0 release.
We’re not simply talking about a collection of open-source tools here. The core of the Cloud Services Platform, Goldberg noted, is “custom configured and battle-tested for enterprises by Google.” In addition, it is deeply integrated with other services in the Google Cloud, including the company’s machine learning tools.
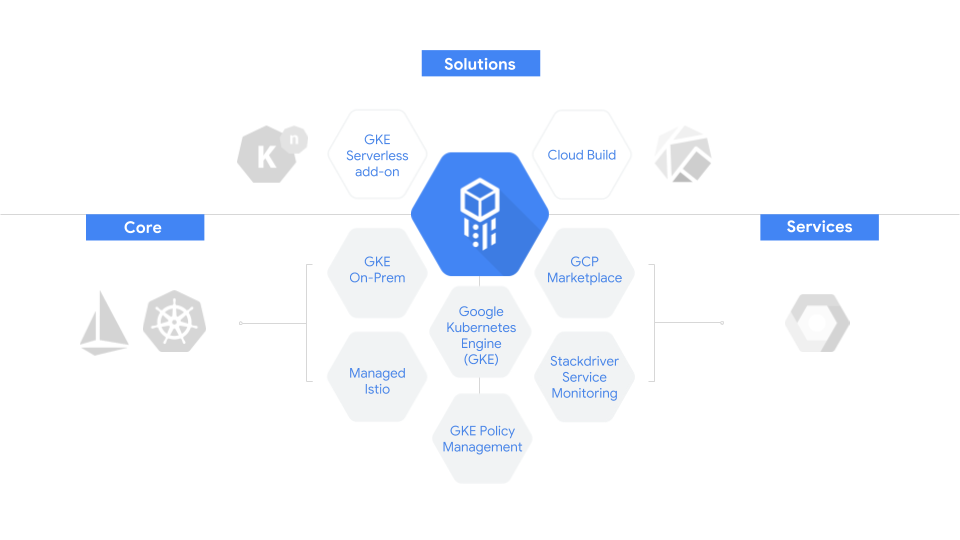
GKE On-Prem
Among these new custom-configured tools are a number of new offerings, which are all part of the larger platform. Maybe the most interesting of these is GKE On-Prem. GKE, the Google Kubernetes Engine, is the core Google Cloud service for managing containers in the cloud. And now Google is essentially bringing this service to the enterprise data center, too.
The service includes access to all of the usual features of GKE in the cloud, including the ability to register and manage clusters and monitor them with Stackdriver, as well as identity and access management. It also includes a direct line to the GCP Marketplace, which recently launched support for Kubernetes-based applications.
Using the GCP Console, enterprises can manage both their on-premise and GKE clusters without having to switch between different environments. GKE on-prem connects seamlessly to a Google Cloud Platform environment and looks and behaves exactly like the cloud version.
Enterprise users also can get access to professional services and enterprise-grade support for help with managing the service.
“Google Cloud is the first and only major cloud vendor to deliver managed Kubernetes on-prem,” Goldberg argued.
GKE Policy Management
Related to this, Google also today announced GKE Policy Management, which is meant to provide Kubernetes administrators with a single tool for managing all of their security policies across clusters. It’s agnostic as to where the Kubernetes cluster is running, but you can use it to port your existing Google Cloud identity-based policies to these clusters. This new feature will soon launch in alpha.
Managed Istio
 The other major new service Google is launching is Managed Istio (together with Apigee API Management for Istio) to help businesses manage and secure their microservices. The open source Istio service mesh gives admins and operators the tools to manage these services and, with this new managed offering, Google is taking the core of Istio and making it available as a managed service for GKE users.
The other major new service Google is launching is Managed Istio (together with Apigee API Management for Istio) to help businesses manage and secure their microservices. The open source Istio service mesh gives admins and operators the tools to manage these services and, with this new managed offering, Google is taking the core of Istio and making it available as a managed service for GKE users.
With this, users get access to Istio’s service discovery mechanisms and its traffic management tools for load balancing and routing traffic to containers and VMs, as well as its tools for getting telemetry back from the workloads that run on these clusters.
In addition to these three main new services, Google is also launching a couple of auxiliary tools around GKE and the serverless computing paradigm today. The first of these is the GKE serverless add-on, which makes it easy to run serverless workloads on GKE with a single-step deploy process. This, Google says, will allow developers to go from source code to container “instantaneously.” This tool is currently available as a preview and Google is making parts of this technology available under the umbrella of its new native open source components. These are the same components that make the serverless add-on possible.
And to wrap it all up, Google also today mentioned a new fully managed continuous integration and delivery service, Google Cloud Build, though the details around this service remain under wraps.
So there you have it. By themselves, all of those announcements may seem a bit esoteric. As a whole, though, they show how Google’s bet on Kubernetes is starting to pay off. As businesses opt for containers to deploy and run their new workloads (and maybe even bring older applications into the cloud), GKE has put Google Cloud on the map to run them in a hosted environment. Now, it makes sense for Google to extend this to its users’ data centers, too. With managed Kubernetes from large and small companies like SUSE, Platform 9, containership is starting to become a big business. It’s no surprise the company that started it all wants to get a piece of this pie, too.


