
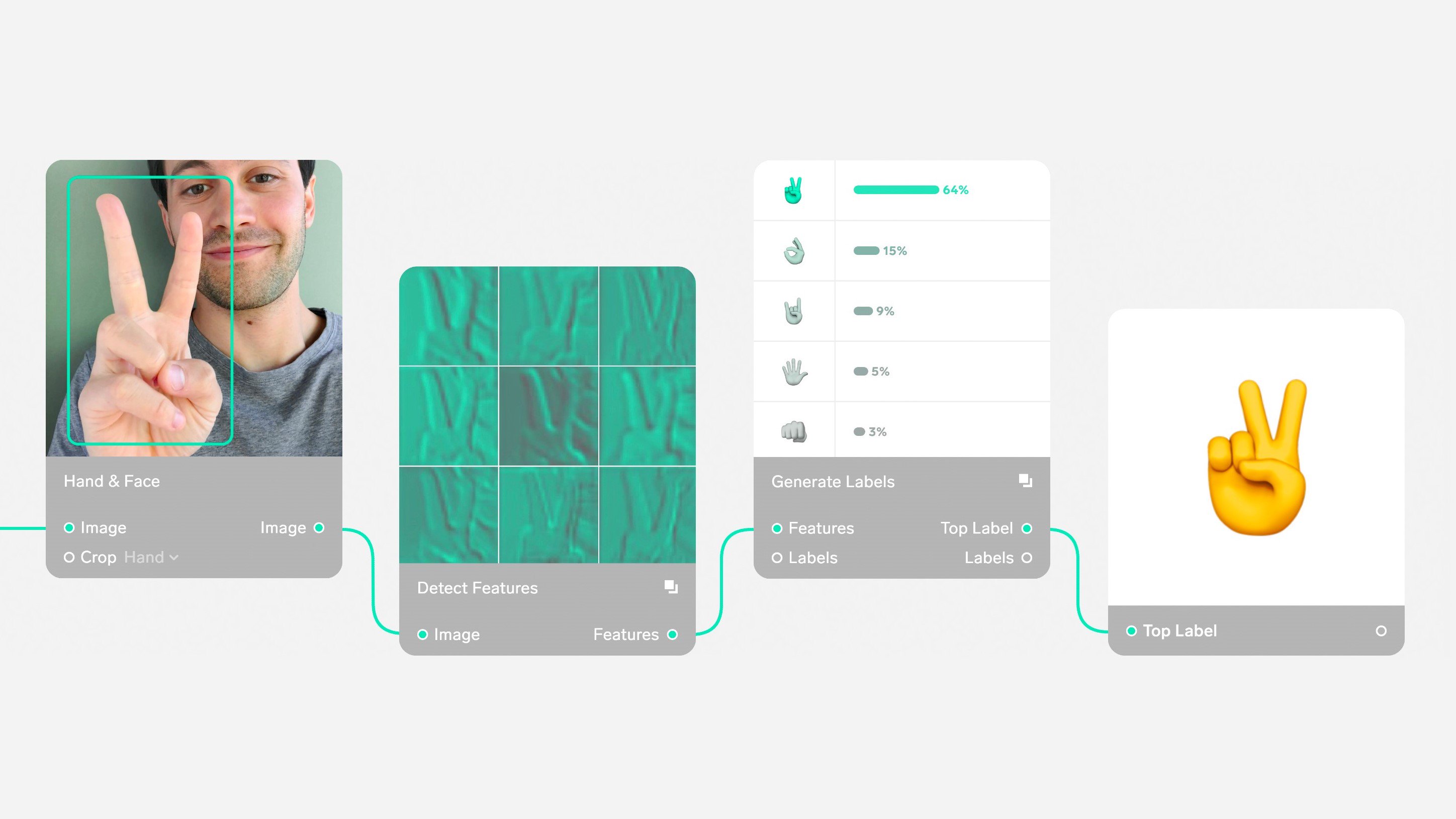
Microsoft today announced that is has acquired Lobe, a startup that lets you build machine learning models with the help of a simple drag-and-drop interface. Microsoft plans to use Lobe, which only launched into beta earlier this year, to build upon its own efforts to make building AI models easier, though, for the time being, Lobe will operate as before.
“As part of Microsoft, Lobe will be able to leverage world-class AI research, global infrastructure, and decades of experience building developer tools,” the team writes. “We plan to continue developing Lobe as a standalone service, supporting open source standards and multiple platforms.”
Lobe was co-founded by Mike Matas, who previously worked on the iPhone and iPad, as well as Facebook’s Paper and Instant Articles products. The other co-founders are Adam Menges and Markus Beissinger.
In addition to Lobe, Microsoft also recently bought Bonsai.ai, a deep reinforcement learning platform, and Semantic Machines, a conversational AI platform. Last year, it acquired Disrupt Battlefield participant Maluuba. It’s no secret that machine learning talent is hard to come by, so it’s no surprise that all of the major tech firms are acquiring as much talent and technology as they can.
“In many ways though, we’re only just beginning to tap into the full potential AI can provide,” Microsoft’s EVP and CTO Kevin Scott writes in today’s announcement. “This in large part is because AI development and building deep learning models are slow and complex processes even for experienced data scientists and developers. To date, many people have been at a disadvantage when it comes to accessing AI, and we’re committed to changing that.”
It’s worth noting that Lobe’s approach complements Microsoft’s existing Azure ML Studio platform, which also offers a drag-and-drop interface for building machine learning models, though with a more utilitarian design than the slick interface that the Lobe team built. Both Lobe and Azure ML Studio aim to make machine learning easy to use for anybody, without having to know the ins and outs of TensorFlow, Keras or PyTorch. Those approaches always come with some limitations, but just like low-code tools, they do serve a purpose and work well enough for many use cases.

