
With 200X the range of Wi-Fi at 1/1000th of the cost of a cellular modem, Helium’s “LongFi” wireless network debuts today. Its transmitters can help track stolen scooters, find missing dogs via IoT collars and collect data from infrastructure sensors. The catch is that Helium’s tiny, extremely low-power, low-data transmission chips rely on connecting to P2P Helium Hotspots people can now buy for $495. Operating those hotspots earns owners a cryptocurrency token Helium promises will be valuable in the future…
The potential of a new wireless standard has allowed Helium to raise $51 million over the past few years from GV, Khosla Ventures and Marc Benioff, including a new $15 million Series C round co-led by Union Square Ventures and Multicoin Capital. That’s in part because one of Helium’s co-founders is Napster inventor Shawn Fanning. Investors are betting that he can change the tech world again, this time with a wireless protocol that like Wi-Fi and Bluetooth before it could unlock unique business opportunities.
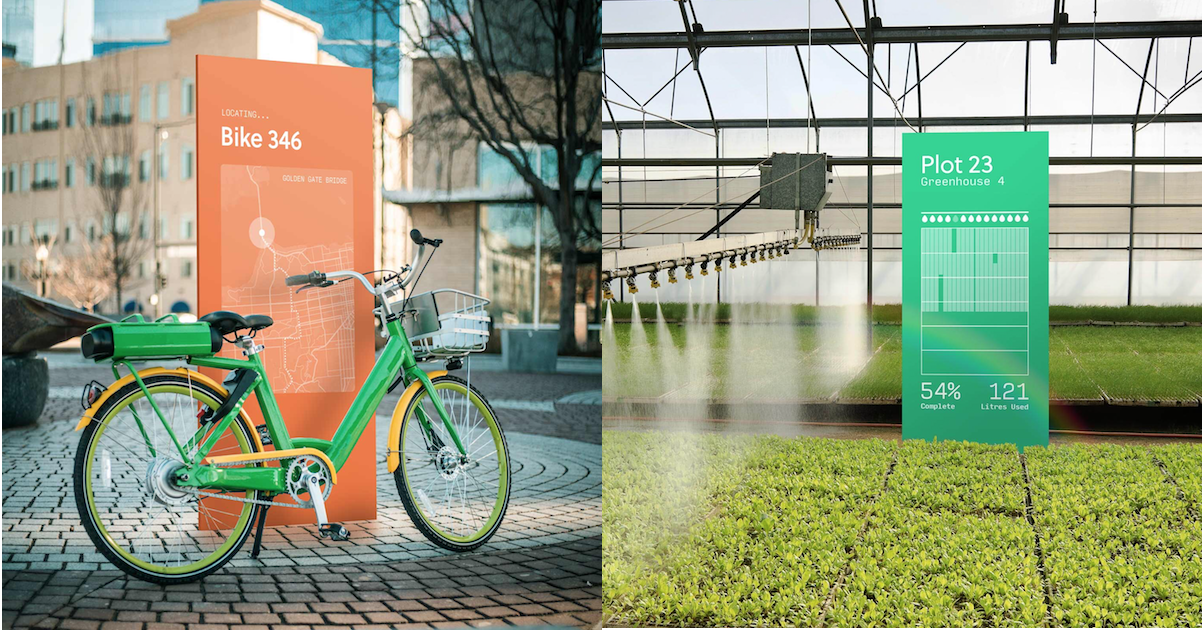

Helium already has some big partners lined up, including Lime, which will test it for tracking its lost and stolen scooters and bikes when they’re brought indoors, obscuring other connectivity, or their battery is pulled, out deactivating GPS. “It’s an ultra low-cost version of a LoJack” Helium CEO Amir Haleem says.
InvisiLeash will partner with it to build more trackable pet collars. Agulus will pull data from irrigation valves and pumps for its agriculture tech business. Nestle will track when it’s time to refill water in its ReadyRefresh coolers at offices, and Stay Alfred will use it to track occupancy status and air quality in buildings. Haleem also imagines the tech being useful for tracking wildfires or radiation.
Haleem met Fanning playing video games in the 2000s. They teamed up with Fanning and Sproutling baby monitor (sold to Mattel) founder Chris Bruce in 2013 to start work on Helium. They foresaw a version of Tile’s trackers that could function anywhere while replacing expensive cell connections for devices that don’t need high bandwith. Helium’s 5 kilobit per second connections will compete with SigFox, another lower-power IoT protocol, though Haleem claims its more centralized infrastructure costs are prohibitive. It’s also facing off against Nodle, which piggybacks on devices’ Bluetooth hardware. Lucky for Helium, on-demand rental bikes and scooters that are perfect for its network have reached mainstream popularity just as Helium launches six years after its start.
Helium says it already pre-sold 80% of its Helium Hotspots for its first market in Austin, Texas. People connect them to their Wi-Fi and put it in their window so the devices can pull in data from Helium’s IoT sensors over its open-source LongFi protocol. The hotspots then encrypt and send the data to the company’s cloud that clients can plug into to track and collect info from their devices. The Helium Hotspots only require as much energy as a 12-watt LED light bulb to run, but that $495 price tag is steep. The lack of a concrete return on investment could deter later adopters from buying the expensive device.
Only 150-200 hotspots are necessary to blanket a city in connectivity, Haleem tells me. But because they need to be distributed across the landscape, so a client can’t just fill their warehouse with the hotspots, and the upfront price is expensive for individuals, Helium might need to sign up some retail chains as partners for deployment. As Haleem admits, “The hard part is the education.” Making hotspot buyers understand the potential (and risks) while demonstrating the opportunities for clients will require a ton of outreach and slick marketing.
Without enough Helium Hotspots, the Helium network won’t function. That means this startup will have to simultaneously win at telecom technology, enterprise sales and cryptocurrency for the network to pan out. As if one of those wasn’t hard enough.

