
Telehealth, or remote, tech-enabled healthcare, has existed for years in primary medical care through companies like Teladoc (NYSE: TDOC), Doctors on Demand and MDLIVE.
In recent years, the application of telehealth had rapidly expanded to address specific chronic and behavioral health issues like mental health, weight loss and nutrition, addiction, diabetes and hypertension, etc. These are real and oftentimes very severe issues faced by people all over the world, yet until now have seen little to no use of technology in providing care.
We believe behavioral health is particularly suited to benefit from the digitization trends COVID-19 has accelerated. Previously, we’ve written about the pandemic’s impact on online learning and education, both for K-12 students and adult learners. But behavioral health is another area impacted by the fundamental change in consumers’ behavior today. Below are four reasons we think the time is now for behavioral health startups — followed by five key factors we think characterize successful companies in this area.
Telehealth can significantly lower the cost of care
Traditional behavioral healthcare is cost-prohibitive for most people. In-person therapy costs $100+ per session in the U.S., and many mental health and substance-use providers don’t accept insurance because they don’t get paid enough by insurers.
By contrast, telehealth reduces overhead costs and scales more effectively. Leveraging technology, providers can treat more patients in less time with almost zero marginal costs. Mobile-based communications enable asynchronous care that further helps providers scale. Access to digital content gives patients on-going support without the need for a human on the other side. This is particularly useful in treating behavioral health issues where ongoing support and motivation may be necessary.
Technology unlocks supply in “shadow markets” of providers
Globally, we face an extreme shortage of behavioral health providers. For example, the United States has fewer than 30,000 licensed psychiatrists (translating to <1 for every 10,000 people). Outside of big cities, the problem gets worse: ~50-60% of nonmetro counties have no psychologists or psychiatrists at all.
Even when providers are available, wait times for appointments are notoriously long. This is a huge issue when behavioral health conditions often require timely intervention.
We are seeing new platforms build large networks of certified coaches, licensed psychologists and psychiatrists, and other providers, aggregating supply in what has historically been a scarce and a highly fragmented provider population.
Behavioral/mental health issues are losing their stigma
We believe the stigma associated with mental illness and other behavioral health conditions is dissipating. More and more public figures are speaking out about their struggle with anxiety, depression, addiction and other behavioral health issues. Our zeitgeist is shifting fast, and there’s an all-time high in people seeking help as the Google Trends data below demonstrates.
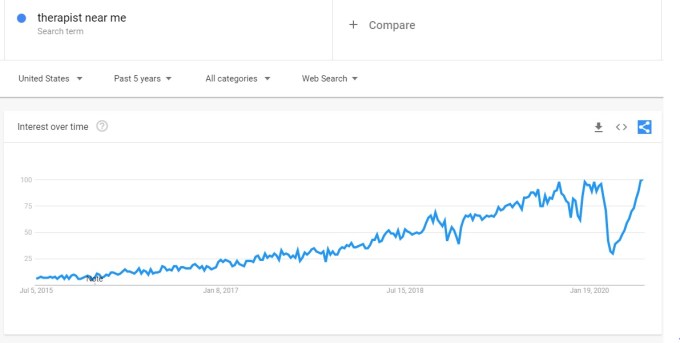
Image Credits: Google
Note: The anomalous dip in March/April ’20 was driven by mandatory shelter-in-place due to COVID-19.

