
California’s new privacy law was years in the making.
The law, California’s Consumer Privacy Act — or CCPA — became law on January 1, allowing state residents to reclaim their right to access and control their personal data. Inspired by Europe’s GDPR, the CCPA is the largest statewide privacy law change in a generation. The new law lets users request a copy of the data that tech companies have on them, delete the data when they no longer want a company to have it, and demand that their data isn’t sold to third parties. All of this is much to the chagrin of the tech giants, some of which had spent millions to comply with the law and have many more millions set aside to deal with the anticipated influx of consumer data access requests.
But to say things are going well is a stretch.
Many of the tech giants that kicked and screamed in resistance to the new law have acquiesced and accepted their fate — at least until something different comes along. The California tech scene had more than a year to prepare, but some have made it downright difficult and — ironically — more invasive in some cases for users to exercise their rights, largely because every company has a different interpretation of what compliance should look like.
Alex Davis is just one California resident who tried to use his new rights under the law to make a request to delete his data. He vented his annoyance on Twitter, saying companies have responded to CCPA by making requests “as confusing and difficult as possible in new and worse ways.”
“I’ve never seen such deliberate attempts to confuse with design,” he told TechCrunch. He referred to what he described as “dark patterns,” a type of user interface design that tries to trick users into making certain choices, often against their best interests.
“I tried to make a deletion request but it bogged me down with menus that kept redirecting… things to be turned on and off,” he said.
Despite his frustration, Davis got further than others. Just as some companies have made it easy for users to opt-out of having their data sold by adding the legally required “Do not sell my info” links on their websites, many have not. Some have made it near-impossible to find these “data portals,” which companies set up so users can request a copy of their data or delete it altogether. For now, California companies are still in a grace period — but have until July when the CCPA’s enforcement provisions kick in. Until then, users are finding ways around it — by collating and sharing links to data portals to help others access their data.
“We really see a mixed story on the level of CCPA response right now,” said Jay Cline, who heads up consulting giant PwC’s data privacy practice, describing it as a patchwork of compliance.
PwC’s own data found that only 40% of the largest 600 U.S. companies had a data portal. Only a fraction, Cline said, extended their portals to users outside of California, even though other states are gearing up to push similar laws to the CCPA.
But not all data portals are created equally. Given how much data companies store on us — personal or otherwise — the risks of getting things wrong are greater than ever. Tech companies are still struggling to figure out the best way to verify each data request to access or delete a user’s data without inadvertently giving it away to the wrong person.
Last year, security researcher James Pavur impersonated his fiancee and tricked tech companies into turning over vast amounts of data about her, including credit card information, account logins and passwords and, in one case, a criminal background check. Only a few of the companies asked for verification. Two years ago, Akita founder Jean Yang described someone hacking into her Spotify account and requesting her account data as an “unfortunate consequence” of GDPR, which mandated companies operating on the continent allow users access to their data.
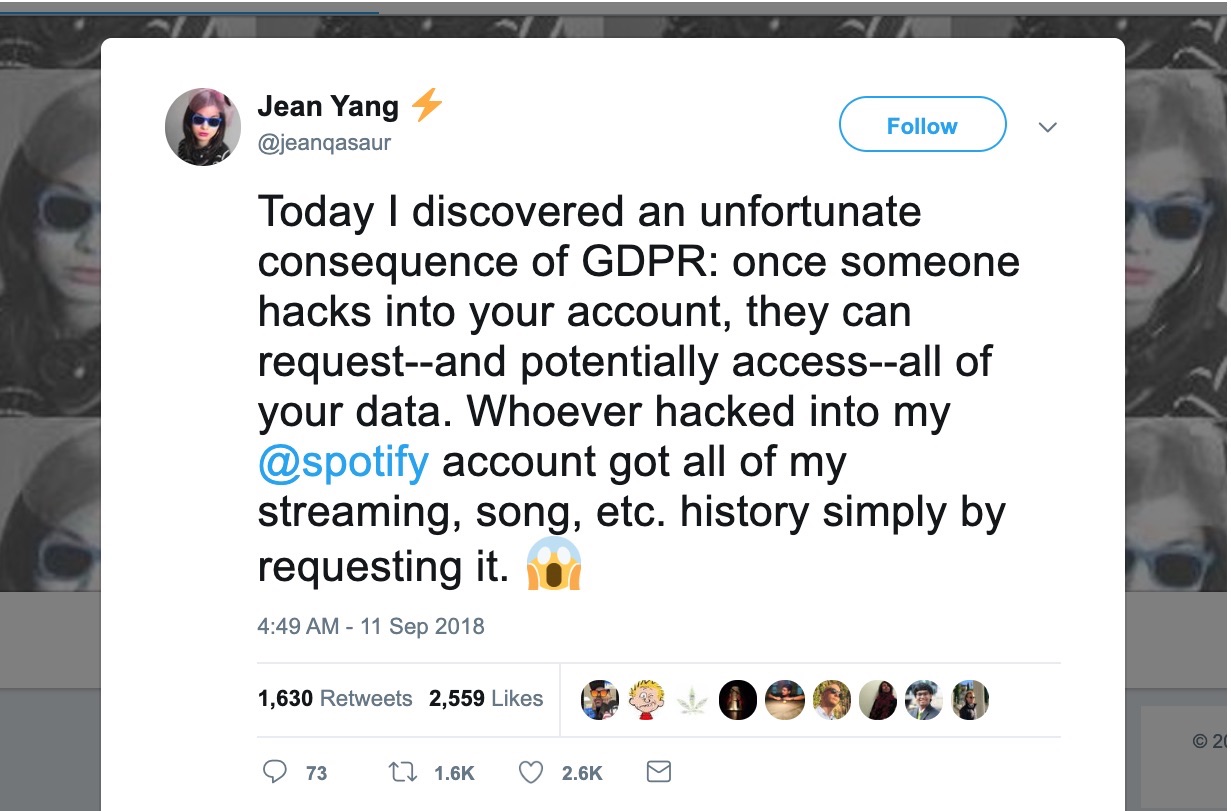
(Image: Twitter/@jeanqasaur)
The CCPA says companies should verify a person’s identity to a “reasonable degree of certainty.” For some that’s just an email address to send the data.
Others require sending in even more sensitive information just to prove it’s them.
Indeed, i360, a little-known advertising and data company, until recently asked California residents for a person’s full Social Security number. This recently changed to just the last four-digits. Verizon (which owns TechCrunch) wants its customers and users to upload their driver’s license or state ID to verify their identity. Comcast asks for the same, but goes the extra step by asking for a selfie before it will turn over any of a customer’s data.
Comcast asks for the same amount of information to verify a data request as the controversial facial recognition startup, Clearview AI, which recently made headlines for creating a surveillance system made up of billions of images scraped from Facebook, Twitter and YouTube to help law enforcement trace a person’s movements.
As much as CCPA has caused difficulties, it has helped forge an entirely new class of compliance startups ready to help large and small companies alike handle the regulatory burdens to which they are subject. Several startups in the space are taking advantage of the $55 billion expected to be spent on CCPA compliance in the next year — like Segment, which gives customers a consolidated view of the data they store; Osano which helps companies comply with CCPA; and Securiti, which just raised $50 million to help expand its CCPA offering. With CCPA and GDPR under their belts, their services are designed to scale to accommodate new state or federal laws as they come in.
Another startup, Mine, which lets users “take ownership” of their data by acting as a broker to allow users to easily make requests under CCPA and GDPR, had a somewhat bumpy debut.
The service asks users to grant them access to a user’s inbox, scanning for email subject lines that contain company names and using that data to determine which companies a user can request their data from or have their data deleted. (The service requests access to a user’s Gmail but the company claims it will “never read” users’ emails.) Last month during a publicity push, Mine inadvertently copied a couple of emailed data requests to TechCrunch, allowing us to see the names and email addresses of two requesters who wanted Crunch, a popular gym chain with a similar name, to delete their data.
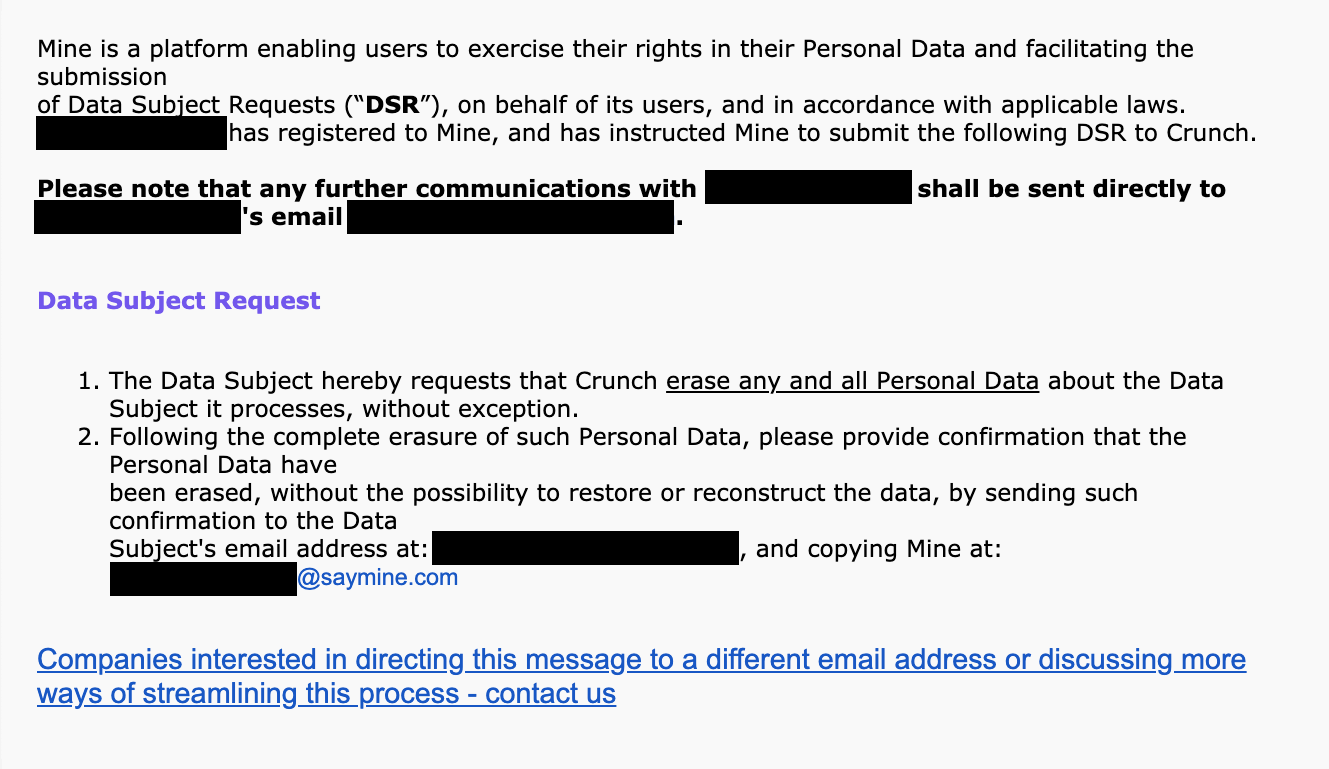
(Screenshot: Zack Whittaker/TechCrunch)
TechCrunch alerted Mine — and the two requesters — to the security lapse.
“This was a mix-up on our part where the engine that finds companies’ data protection offices’ addresses identified the wrong email address,” said Gal Ringel, co-founder and chief executive at Mine. “This issue was not reported during our testing phase and we’ve immediately fixed it.”
For now, many startups have caught a break.
The smaller, early-stage startups that don’t yet make $25 million in annual revenue or store the personal data on more than 50,000 users or devices will largely escape having to immediately comply with CCPA. But it doesn’t mean startups can be complacent. As early-stage companies grow, so will their legal responsibilities.
“For those who did launch these portals and offer rights to all Americans, they are in the best position to be ready for these additional states,” said Cline. “Smaller companies in some ways have an advantage for compliance if their products or services are commodities, because they can build in these controls right from the beginning,” he said.
CCPA may have gotten off to a bumpy start, but time will tell if things get easier. Just this week, California’s attorney general Xavier Becerra released newly updated guidance aimed at trying to “fine tune” the rules, per his spokesperson. It goes to show that even California’s lawmakers are still trying to get the balance right.
But with the looming threat of hefty fines just months away, time is running out for the non-compliant.

