
It’s passive zombie-feed scrolling, not active communication with friends, that hurts our health, according to studies Facebook has been pointing to for the last seven months. Yet it’s treating all our social networking the same with today’s launch of its digital well-being screen-time management dashboards for Facebook and Instagram in the U.S. before rolling them out to everyone in the coming weeks.
Giving users a raw count of the minutes they’ve spent in their apps each day in the last week plus their average across the week is a good start to making users more mindful. But by burying them largely out of sight, giving them no real way to compel less usage and not distinguishing between passive and active behavior, they seem destined to be ignored while missing the point the company itself stresses.
TechCrunch scooped the designs of the two separate but identical Instagram and Facebook tools over the past few months thanks to screenshots from the apps’ code generated by Jane Manchun Wong. What’s launching today is what we saw, with the dashboards located in Facebook’s “Settings” -> “Your Time On Facebook” and Instagram’s “Settings” -> “Your Activity.”

Unfortunately, you’ll only see info about your usage on the mobile app on that device. It won’t include your minutes spent on desktop, where these features don’t appear, what you do on your tablet or info about your usage across the Facebook family of apps. There are no benchmarks about how long other people your age or in your country spend in the apps. All of these would make nice improvements to the dashboards.
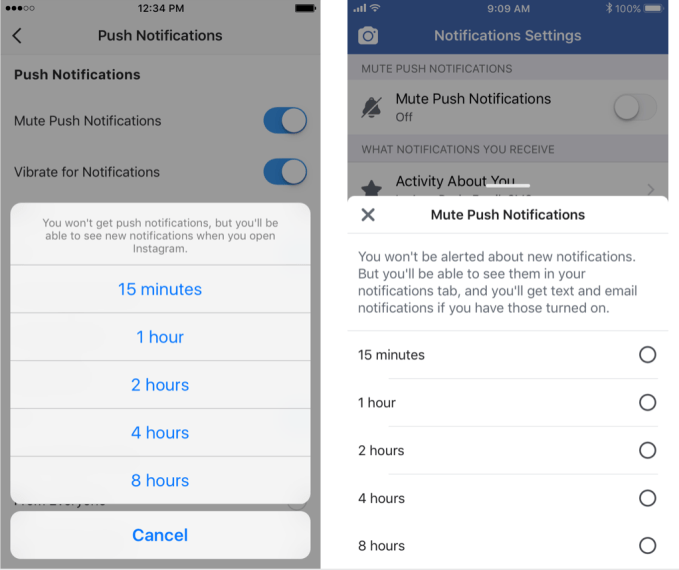
Beyond the daily and average minute counts, you can set a daily “limit” in minutes, after which either app will send you a reminder that you’ve crossed your self-imposed threshold. But they won’t stop you from browsing and liking, or force you to dig into the Settings menu to extend your limit. You’ll need the willpower to cut yourself off. The tools also let you mute push notifications (you’ll still see in-app alerts), but only for as much as 8 hours. If you want anything more permanent, you’ll have to dig into their separate push notification options menu or your phone’s settings.
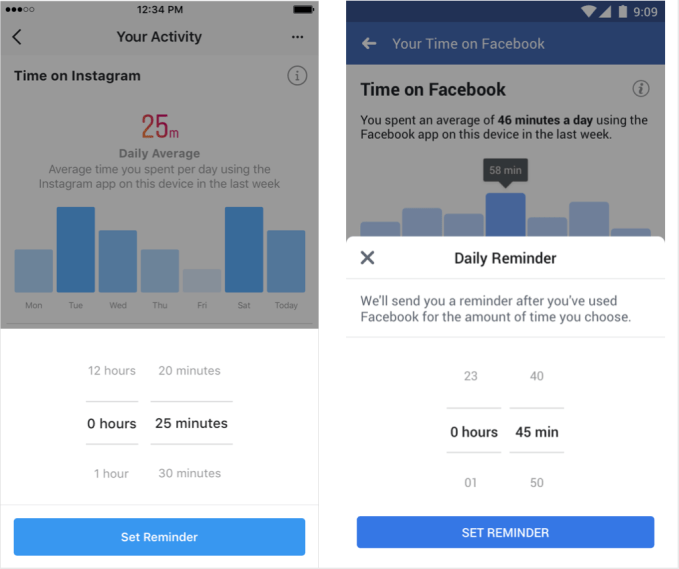
The announcement follows Instagram CEO Kevin Systrom’s comments about our original scoop, where he tweeted “It’s true . . . We’re building tools that will help the IG community know more about the time they spend on Instagram – any time should be positive and intentional . . . Understanding how time online impacts people is important, and it’s the responsibility of all companies to be honest about this. We want to be part of the solution. I take that responsibility seriously.”
Users got their first taste of Instagram trying to curtail overuse with its “You’re All Caught Up” notices that show when you’ve seen all your feed posts from the past two days. Both apps will now provide callouts to users teaching them about the new activity-monitoring tools. Facebook says it has no plans to use whether you open the tools or set daily limits to target ads. It will track how people use the tools to tweak the designs, but it sounds like that’s more about what time increments to show in the Daily Reminder and Mute Notifications options than drastic strengthening of their muscle. Facebook will quietly keep a tiny fraction of users from getting the features to measure if the launch impacts behavior.
“It’s really important for people who use Instagram and Facebook that the time they spend with us is time well spent,” Ameet Ranadive, Instagram’s Product Director of Well-Being, told reporters on a conference call. “There may be some trade-off with other metrics for the company and that’s a trade-off we’re willing to live with, because in the longer term we think this is important to the community and we’re willing to invest in it.”
Facebook needs stronger screen time tools that deter passive browsing
Facebook has already felt some of the brunt of that trade-off. It’s been trying to improve digital well-being by showing fewer low-quality viral videos and clickbait news stories, and more from your friends since a big algorithm change in January. That’s contributed to a flatlining of its growth in North America, and even a temporary drop of 700,000 users early this year, while it also lost 1 million users in Europe this past quarter. That led to Facebook’s slowest user growth rates in history, triggering a 20 percent, $120 billion market cap drop in its share price. “The changes to the News Feed back in January were one step . . . giving people a sense of their time so they’re more mindful of it is the second step,” says Ranadive.
The fact that Facebook is willing to put its finances on the line for digital well-being is a great step. It’s a smart long-term business decision, too. If we feel good about our overall usage, we won’t ditch the apps entirely and could keep seeing their ads for another decade. But it’s likely to be changes to the Facebook and Instagram feeds that prioritize content you’ll comment on rather than look at and silently scroll past that will contribute more to healthy social networking than today’s toothless tools.
While iOS 12’s Screen Time and Android’s new Digital Wellbeing features both count your minutes on different apps too, they offer more drastic ways to enforce your own good intentions. iOS will deliver a weekly usage report to remind you the features exist. Android’s is best-in-class because it grays out an app’s icon and requires you to open your settings to unlock an app after you exceed your daily limit.
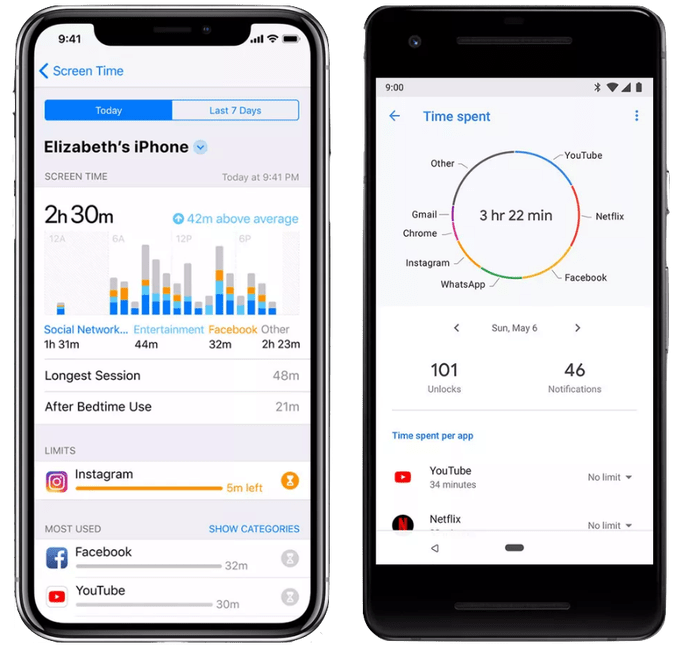
iOS Screen Time (left) and Android Digital Wellbeing (right)
To live up to the responsibility Systrom promised, Facebook and Instagram will have to do more to actually keep us mindful of the time we spend in their apps and help us help ourselves. Let us actually lock ourselves out of the apps, turn them grayscale, fade their app icons or persistently show our minute count onscreen once we pass our limit. Anything to make being healthy on their apps something you can’t just ignore like any other push notification.
Or follow the research and have the dashboards actually divide our sharing, commenting and messaging time from our feed scrolling, Stories tapping, video watching and photo stalking. The whole point is that social networking isn’t all bad, but there are behaviors that hurt. Most of us aren’t going to give up Facebook and Instagram. Even just trying to spend less time on them is difficult. But by guiding us toward the activities that interconnect us rather than isolate us, Facebook could get us to shift our time in the right direction.

