
Powerful enough to cross oceans, delivering aid

Sergey Brin’s secretive airship company LTA Research and Exploration is planning to power a huge disaster relief airship with an equally record-breaking hydrogen fuel cell.
A job listing from the company, which is based in Mountain View, California and Akron, Ohio, reveals that LTA wants to configure a 1.5-megawatt hydrogen propulsion system for an airship to deliver humanitarian aid and revolutionize transportation. While there are no specs tied to the job listing, such a system would likely be powerful enough to cross oceans. Although airships travel much slower than jet planes, they can potentially land or deliver goods almost anywhere.
Hydrogen fuel cells are an attractive solution for electric aviation because they are lighter and potentially cheaper than lithium-ion batteries. However, the largest hydrogen fuel cell to fly to date is a 0.25-megawatt system (250 kilowatts) in ZeroAvia’s small passenger plane last September. LTA’s first crewed prototype airship, called Pathfinder 1, will be powered by batteries when it takes to the air, possibly this year. FAA records show that the Pathfinder 1 has 12 electric motors and would be able to carry 14 people.
That makes it about the same size as the only passenger airship operating today, the Zeppelin NT, which conducts sightseeing tours in Germany and Switzerland. The Pathfinder 1 also uses some Zeppelin components in its passenger gondola.
Image Credits: LTA Patent US 2019/0112023 A1
Since the Hindenburg disaster in 1937, most airships, including LTA’s, have used non-flammable helium as a lifting gas. But using hydrogen for fuel still makes sense, according to Professor Dr. Josef Kallo of the German Aerospace Center, which is developing its own 1.5 MW fuel cell to power a 60-seater regional electric aircraft.
“Where we could go something like 125 miles with batteries, we should be able to go nearly 1,000 miles using hydrogen,” Kallo said. “And airships are even more perfect for the efficiency of fuel cells.”
Fuel cells combine hydrogen and oxygen to produce water and electricity, but are traditionally heavy and complex. Putting one in an aircraft adds extra complications such as safely transporting the liquid hydrogen in fuel tanks, storing the water produced and dealing with a lot of waste heat.
LTA’s first fuel cell will be a 0.75 MW system, built by a third party and retrofitted into one of its existing prototypes, according to the job listing. That is unlikely to happen this year, however. A planned Pathfinder 3 airship, which will run on batteries, still has not been registered with the FAA.
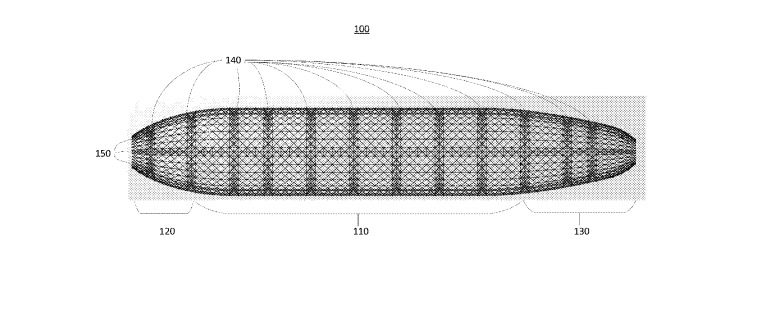
Image Credits: LTA Research Patent US 2019/0112023 A1
“Functionality wise, there is no showstopper to using a hydrogen fuel cell,” Kallo said. “The challenge is to find someone who can afford not to look at the business case, because I don’t think it works out from an economic perspective. Maybe Sergey Brin can afford to do that.”
Brin is currently the ninth richest person in the world, with a net worth of over $86 billion. LTA’s website says the initial use case for its aircraft will be “humanitarian disaster response and relief efforts, especially in remote areas that cannot be easily accessed by plane and boat due to limited or destroyed infrastructure.” Ultimately, it intends to create a family of zero emissions aircraft for global cargo and passenger travel.
LTA has already started its charitable work, producing more than 5 million face masks for first responders during the COVID-19 pandemic, and donating nearly $3 million last year to the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees.
LTA is likely to operate closely with Brin’s nonprofit disaster relief force, Global Support and Development (GSD), which is based just a few miles from LTA’s Mountain View hangars. GSD has deployed medics and ex-military personnel to numerous natural disasters over the past five years. It prides itself on its ability to arrive before traditional NGOs, on occasion even using Brin’s own superyacht. Tax records show that Brin is by far the largest funder of GSD, giving it at least $7.5 million in 2019.

